The World Health Organisation’s research paper ‘Natural Ventilation for Infection Control in Healthcare Settings’ specifies how important ventilation is in controlling the spread of germs in medical facilities. A proper flow of air through treatment and recovery spaces helps reduce the growth of infectious illnesses while also stimulating the natural recovery process.
This makes structural principles that incorporate natural airflow in perfect healthcare facility design vital. We took an in-depth look into this building trend, known as ‘breathing architecture’ to determine why this design principle contributes to a more effective medical space.
Healthcare facility design that aids health
It may seem unusual, but even the most minor architectural elements of your medical facility can contribute to faster patient recovery time, and improved mental and physical well-being. The basic health elements that apply in everyday life are even more applicable in healthcare facilities. We still need ample natural light exposure and regular airflow to minimise the risk of infections spreading. This makes architectural designs that consider these factors an excellent long-term investment.
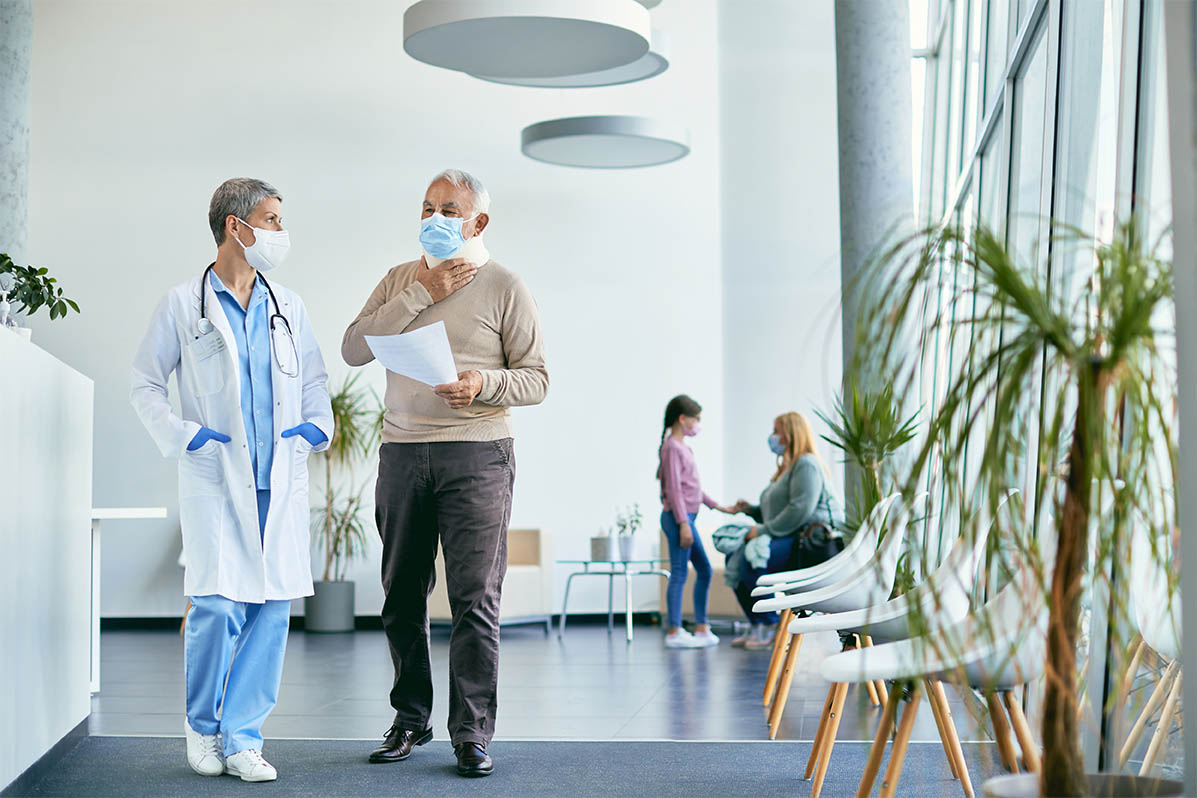
 Natural air flow is vital to improving a patient’s recovery and mental well-being.
Natural air flow is vital to improving a patient’s recovery and mental well-being.
What is breathing architecture and why is it a positive influence on patient health?
Breathing architecture is a principle that employs structural and aesthetic strategies to maximise the flow of natural air and improve mechanical ventilation for better indoor air quality. These practices contribute to beautiful buildings with a more ‘open’ feel and improved breathability.
Design choices include:
- Designing spaces with fewer walls, pillars and other hindrances to airflow.
- Incorporating more windows and access points to the outside in the building plans.
- Analysing natural windflow tunnels in the early facility design phase and arranging your floor plan to place areas that require high airflow the most around these spaces. For example, locating patient recovery rooms here would be more advantageous than incubators or laboratories that require stable environmental conditions.
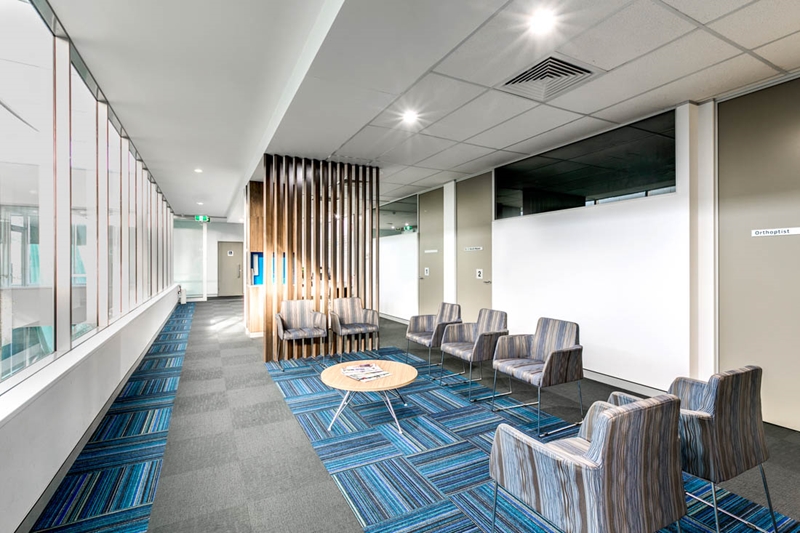 Open-plan floor space is central to breathing architecture design.
Open-plan floor space is central to breathing architecture design.The positive influences of breathing architecture to maximise airflow and ventilation include:
- Breathing architecture helps to dilute or remove other air pollutants from high-traffic areas, as well as naturally reduce the risk of infections spreading.
- Breathing architecture incidentally also considers natural light as an important design element. Natural light is well-documented in numerous studies, including one conducted by Northwestern University on natural light in the office, as essential to better healthcare facility design.
- Improved mechanical ventilation through breathing architecture elements in healthcare facility design can help to reduce a building’s HVAC costs.
Incorporating breathing architecture into healthcare facility design
Employing elements of breathing architecture in healthcare facility design is easier when you enlist the help of medical architecture experts. Space for Health has several relevant offerings, including feasibility and design development services, offering guidance on how you can maximise natural airflow in your healthcare facility.
For more information about design principles that can improve the well-being of your medical facility patients, contact the Space for Health team today.